Bootstrap Breakpoints Using
Introduction
Having in idea each of the achievable screen widths where our website pages could eventually feature it is necessary to compose them in a method granting undisputed sharp and impressive appeal-- generally utilizing the assistance of a highly effective responsive framework like probably the most well-known one-- the Bootstrap framework in which most current edition is right now 4 alpha 6. However, what it actually handles to assist the web pages pop in excellent on any display-- let's have a glance and discover.
The major standard in Bootstrap ordinarily is positioning certain ordination in the limitless possible gadget screen sizes (or viewports) placing them in a number of ranges and styling/rearranging the content as needed. These particular are also termed grid tiers or else display screen sizes and have evolved quite a little via the numerous editions of the most prominent recently responsive framework around-- Bootstrap 4.
The way to use the Bootstrap Breakpoints Grid:
Commonly the media queries become defined with the following structure @media ( ~screen size condition ~) ~ styling rules to get applied if the condition is met ~. The conditions can certainly limit one end of the interval like min-width: 768px of both of them like min-width: 768px - while the viewport size in within or else equivalent to the values in the demands the rule uses. As media queries come with the CSS language certainly there can be much more than one query for a single viewport width-- if so the one particular being read by the internet browser last has the word-- much like regular CSS rules.
Differences of Bootstrap editions
In Bootstrap 4 unlike its own forerunner there are 5 display widths however given that the latest alpha 6 build-- basically only 4 media query groups-- we'll get back to this in just a sec. Considering that you most likely know a .row in bootstrap includes column features having the actual page web content which can easily span up to 12/12's of the detectable width offered-- this is oversimplifying but it is actually another thing we are certainly discussing here. Every column element get specified by one of the column classes incorporating .col - for column, display size infixes specifying down to which display dimension the content will stay inline and will span the whole horizontal width below and a number showing how many columns will the element span when in its own screen dimension or just above.
Display measurements
The screen sizes in Bootstrap typically use the min-width requirement and come as follows:
Extra small – widths under 576px –This screen actually doesn't have a media query but the styling for it rather gets applied as a common rules getting overwritten by the queries for the widths above. What's also new in Bootstrap 4 alpha 6 is it actually doesn't use any size infix – so the column layout classes for this screen size get defined like col-6 - such element for example will span half width no matter the viewport.
Extra small-- widths below 576px-- This display in fact doesn't possess a media query but the designing for it instead gets used as a standard regulations being overwritten by the queries for the sizes just above. What's likewise new inside Bootstrap 4 alpha 6 is it really does not operate any kind of dimension infix-- so the column style classes for this screen size get defined such as col-6 - this type of element as an example will span half width despite of the viewport.
Small screens-- applies @media (min-width: 576px) ... and the -sm- infix. { For example element having .col-sm-6 class will certainly span half size on viewports 576px and wider and full width below.
Medium screens-- employs @media (min-width: 768px) ... as well as the -md- infix. As an example element having .col-md-6 class will cover half width on viewports 768px and larger and full width below-- you've quite possibly got the drill actually.
Large display screens - employs @media (min-width: 992px) ... and the -lg- infix.
And lastly-- extra-large displays - @media (min-width: 1200px) ...-- the infix here is -xl-
Responsive breakpoints
Since Bootstrap is undoubtedly created to be mobile first, we employ a number of media queries to establish sensible breakpoints for styles and softwares . These kinds of Bootstrap Breakpoints Responsive are normally accordinged to minimal viewport sizes as well as enable us to adjust up factors while the viewport changes.
Bootstrap primarily employs the following media query stretches-- or breakpoints-- in source Sass data for layout, grid system, and elements.
// Extra small devices (portrait phones, less than 576px)
// No media query since this is the default in Bootstrap
// Small devices (landscape phones, 576px and up)
@media (min-width: 576px) ...
// Medium devices (tablets, 768px and up)
@media (min-width: 768px) ...
// Large devices (desktops, 992px and up)
@media (min-width: 992px) ...
// Extra large devices (large desktops, 1200px and up)
@media (min-width: 1200px) ...Given that we formulate resource CSS in Sass, all of media queries are simply obtainable via Sass mixins:
@include media-breakpoint-up(xs) ...
@include media-breakpoint-up(sm) ...
@include media-breakpoint-up(md) ...
@include media-breakpoint-up(lg) ...
@include media-breakpoint-up(xl) ...
// Example usage:
@include media-breakpoint-up(sm)
.some-class
display: block;We in some cases use media queries which proceed in the some other course (the provided display screen size or even smaller sized):
// Extra small devices (portrait phones, less than 576px)
@media (max-width: 575px) ...
// Small devices (landscape phones, less than 768px)
@media (max-width: 767px) ...
// Medium devices (tablets, less than 992px)
@media (max-width: 991px) ...
// Large devices (desktops, less than 1200px)
@media (max-width: 1199px) ...
// Extra large devices (large desktops)
// No media query since the extra-large breakpoint has no upper bound on its widthOnce again, such media queries are as well provided by means of Sass mixins:
@include media-breakpoint-down(xs) ...
@include media-breakpoint-down(sm) ...
@include media-breakpoint-down(md) ...
@include media-breakpoint-down(lg) ...There are also media queries and mixins for aim a single part of screen scales working with the lowest and highest Bootstrap Breakpoints Table widths.
// Extra small devices (portrait phones, less than 576px)
@media (max-width: 575px) ...
// Small devices (landscape phones, 576px and up)
@media (min-width: 576px) and (max-width: 767px) ...
// Medium devices (tablets, 768px and up)
@media (min-width: 768px) and (max-width: 991px) ...
// Large devices (desktops, 992px and up)
@media (min-width: 992px) and (max-width: 1199px) ...
// Extra large devices (large desktops, 1200px and up)
@media (min-width: 1200px) ...These kinds of media queries are as well readily available through Sass mixins:
@include media-breakpoint-only(xs) ...
@include media-breakpoint-only(sm) ...
@include media-breakpoint-only(md) ...
@include media-breakpoint-only(lg) ...
@include media-breakpoint-only(xl) ...Also, media queries can span several breakpoint sizes:
// Example
// Apply styles starting from medium devices and up to extra large devices
@media (min-width: 768px) and (max-width: 1199px) ...
<code/>
The Sass mixin for focus on the identical display screen dimension variety would certainly be:
<code>
@include media-breakpoint-between(md, xl) ...Conclusions
Together with identifying the size of the webpage's features the media queries take place all over the Bootstrap framework ordinarily having defined by means of it - ~screen size ~ infixes. Once seen in numerous classes they must be interpreted just like-- no matter what this class is executing it is actually handling it down to the screen width they are referring.
Review several video clip training relating to Bootstrap breakpoints:
Related topics:
Bootstrap breakpoints authoritative documents"

Bootstrap Breakpoints difficulty
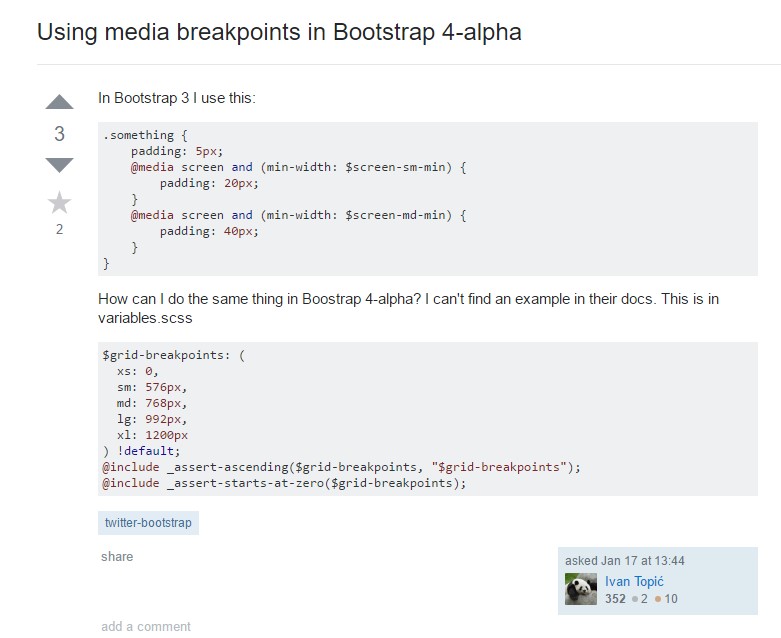
Alter media query breakpoint systems from em to px